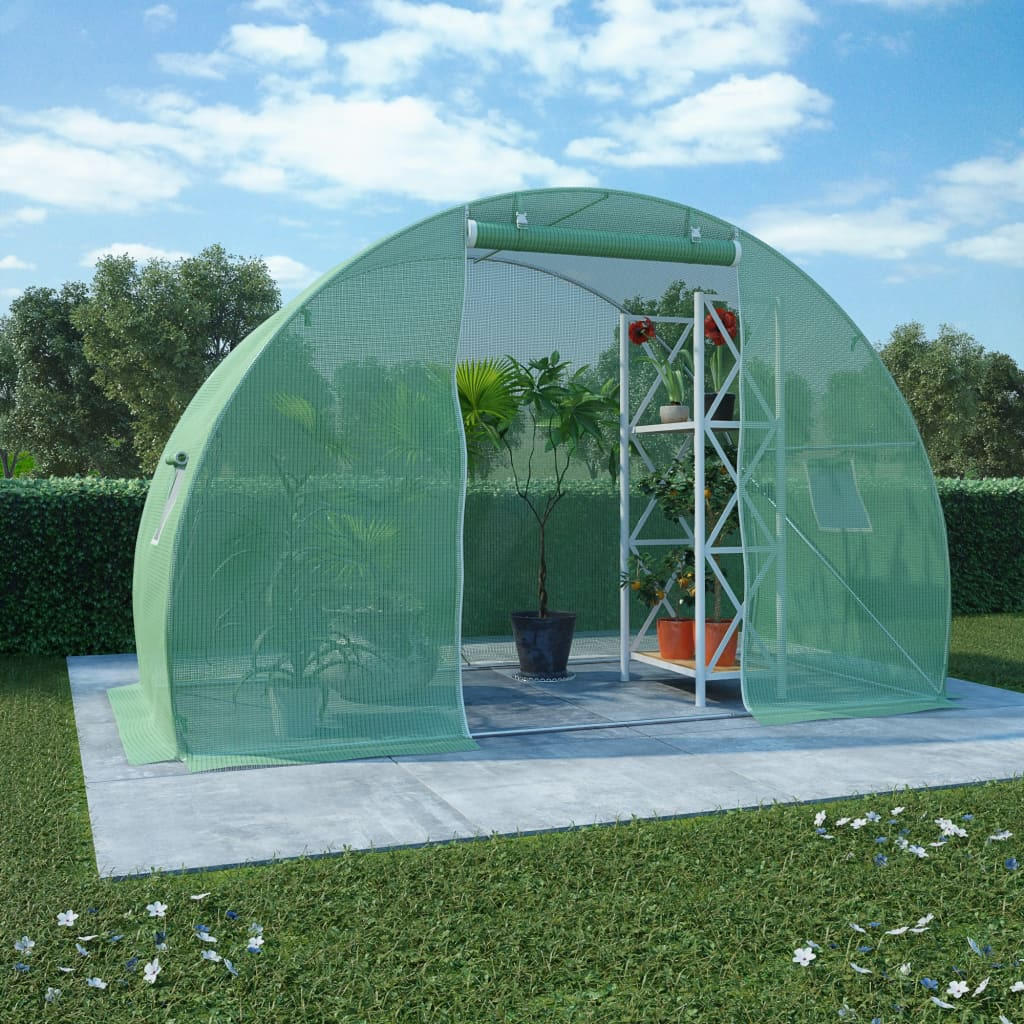
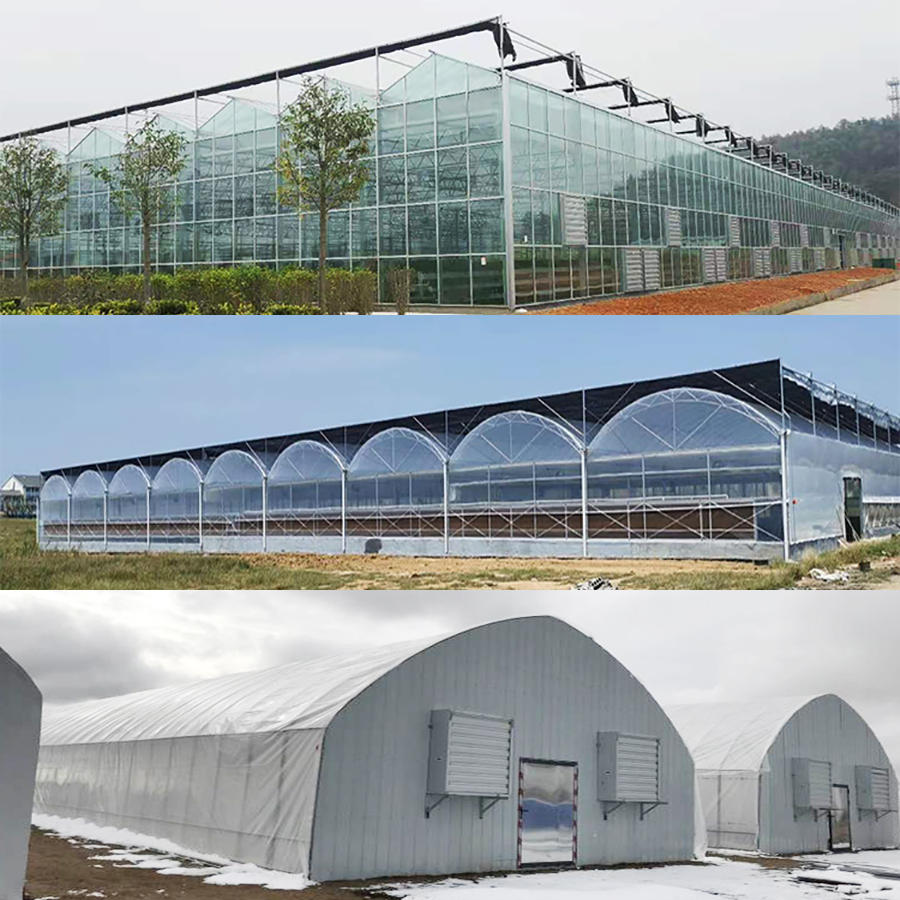
Our Service
Our factories are supervised carefully, we have strict quality assurance test and lab test and multiple inspections. This means we find glitches before they become problems, thus preventing you from disastrous quality problems. We guarantee your satisfaction from start to finish.
We helped a lot of clients creating their own brand with our strict quality raw material select, higher quality production technology and professional services.
We could also make customized products according to your needs. you can talk to our customer service center about your sourcing requirements, whether selecting a current product from our catalog or seeking assistance for your application.


 英语
英语 俄语
俄语 德语
德语 西班牙语
西班牙语 法语
法语






















.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)



